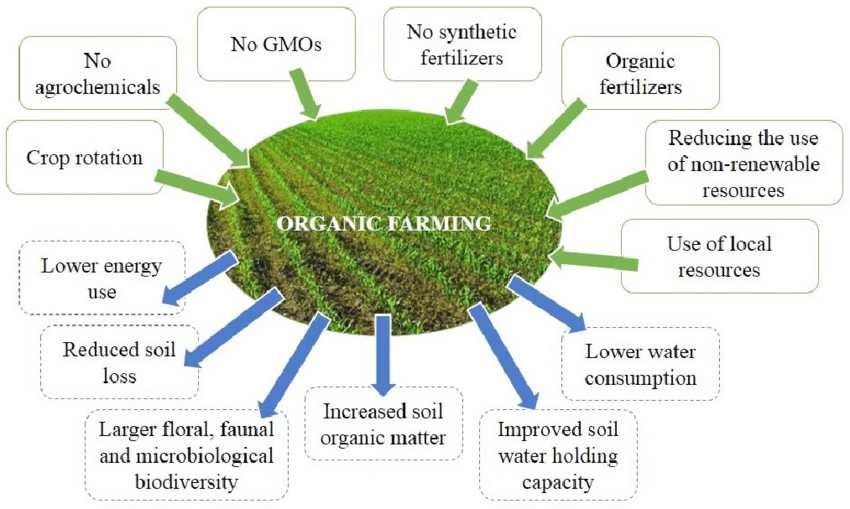
Organic farming facts reveal a compelling narrative of sustainable agriculture practices that prioritize environmental stewardship, biodiversity conservation, and human health. Organic farming, characterized by the avoidance of synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs), stands in contrast to conventional agriculture. Instead, organic farming emphasizes natural inputs like compost, crop rotation, and biological pest control to enhance soil fertility and maintain ecosystem balance.

One of the standout organic farming facts is its positive impact on soil health. Organic practices promote soil structure by fostering microbial activity and organic matter content, which improves nutrient cycling and water retention. Studies consistently show that organic soils have higher levels of beneficial microorganisms and greater biodiversity compared to conventional soils, contributing to long-term soil fertility and resilience.
Another compelling aspect of organic farming facts lies in its environmental benefits. By eschewing synthetic chemicals, organic farming reduces water and air pollution while conserving biodiversity. Pesticide-free practices protect beneficial insects, birds, and wildlife, supporting ecosystem services such as pollination and natural pest control. Organic farms also tend to have lower carbon footprints due to reduced reliance on fossil fuel-intensive synthetic inputs, thereby mitigating greenhouse gas emissions and climate change impacts.
Organic farming facts extend beyond environmental benefits to encompass nutritional advantages. Research indicates that organic fruits, vegetables, and grains often contain higher levels of antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals compared to conventionally grown counterparts. This nutritional superiority is attributed to the absence of synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, which may interfere with plant nutrient uptake and overall crop quality in conventional farming systems.
Moreover, organic farming facts underscore its role in promoting animal welfare and humane livestock practices. Organic standards mandate access to outdoor areas and pasture for livestock, prohibiting the use of growth hormones and routine antibiotics. These practices support healthier animals and contribute to higher-quality organic meat, dairy, and egg products sought after by consumers concerned with food safety and animal welfare.
Economically, organic farming continues to gain traction globally, driven by increasing consumer demand for organic products and the potential for premium pricing. While initial conversion to organic farming may pose challenges such as higher labor costs and transition periods, studies indicate that organic farms can achieve comparable or even higher profitability over time, especially when factoring in long-term soil health benefits and reduced input costs.
Policy and regulation also shape the landscape of organic farming. Governments worldwide have developed organic certification standards to ensure integrity and transparency in organic labeling and marketing. These standards help consumers make informed choices and provide assurance that organic products meet stringent production requirements, including annual inspections and adherence to organic farming principles.
In summary, organic farming facts underscore a holistic approach to agriculture that prioritizes sustainability, health, and environmental stewardship. As global challenges like climate change, soil degradation, and food security intensify, organic farming offers a viable solution by promoting resilient farming systems that nurture both people and planet. Embracing organic principles not only supports healthier ecosystems and communities but also fosters a sustainable food future for generations to come.









