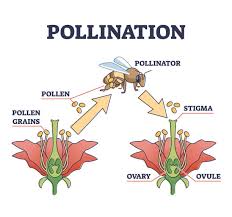
`Organic farming pollinators play a crucial role in the success of organic agriculture, influencing crop yields, plant health, and overall ecosystem balance. In organic farming, the focus on sustainability and environmental health extends to the management and protection of pollinators, which are essential for the reproduction of many plants. Organic farming pollinators, including bees, butterflies, and other beneficial insects, contribute significantly to the productivity of organic farms by facilitating the pollination process. This natural service is vital for the cultivation of a wide range of fruits, vegetables, and nuts, making organic farming pollinators indispensable for achieving high-quality and abundant harvests.

The relationship between organic farming and pollinators is symbiotic, with each benefiting from the other’s presence. Organic farming practices support pollinators by creating a habitat that is free from synthetic pesticides and chemical fertilizers. This not only protects pollinators from harmful chemicals but also ensures that they have access to diverse and nutritious food sources. Organic farms often feature a variety of flowering plants, cover crops, and hedgerows that provide essential nectar and pollen for pollinators throughout the growing season. By fostering such environments, organic farming enhances the health and effectiveness of pollinators, leading to more efficient and successful pollination.
One of the most notable organic farming pollinators is the honeybee, which is crucial for the pollination of numerous crops. Honeybees are highly efficient at transferring pollen between flowers, which increases fruit and seed production. In organic farming systems, beekeeping practices are often integrated to support honeybee populations and ensure their well-being. Providing habitat and resources for honeybees, such as nesting sites and access to clean water, can significantly boost their numbers and activity levels, enhancing overall crop yields. Additionally, organic farmers may use practices like planting wildflower strips and maintaining natural vegetation to attract and support honeybees.
Another important group of organic farming pollinators includes wild bees, which comprise a diverse range of species with varying pollination behaviors. Wild bees, such as bumblebees and solitary bees, are valuable contributors to the pollination of crops and wild plants. Organic farming practices that promote biodiversity and habitat complexity are particularly beneficial for wild bee populations. By planting a variety of flowering plants and creating diverse habitats, organic farmers can support wild bees and enhance their pollination services. This approach not only benefits crop production but also helps preserve the overall health of the ecosystem.
Butterflies and moths are also significant organic farming pollinators, as they visit flowers in search of nectar and contribute to the pollination of various crops. These insects are attracted to colorful and aromatic flowers, making them important for the pollination of plants that produce fruits, vegetables, and herbs. Organic farming practices that include a wide range of flowering plants and provide natural habitat features can attract and support butterfly and moth populations. By maintaining a diverse and flowering-rich environment, organic farmers can enhance the presence and activity of these important pollinators.
Effective management of organic farming pollinators involves understanding their needs and implementing practices that support their health and productivity. This includes minimizing habitat disturbances, avoiding pesticide use, and providing ample forage and nesting sites. Organic farmers can also engage in habitat restoration efforts, such as planting native plants and creating pollinator-friendly landscapes, to further support pollinator populations. Monitoring pollinator activity and health can help farmers make informed decisions about how to best support and protect these valuable insects.
In conclusion, organic farming pollinators are integral to the success of organic agriculture, providing essential pollination services that enhance crop yields and plant health. By adopting practices that protect and support pollinators, organic farmers can create thriving environments that benefit both their crops and the broader ecosystem. The interplay between organic farming and pollinators underscores the importance of sustainable and environmentally friendly practices in agriculture. As the demand for organic produce grows, the role of pollinators in organic farming will continue to be a key factor in achieving productive and resilient farming systems.









