Smart organic farming and healthcare are two distinct fields that can have complementary relationships.
Smart organic farming is a sustainable and environmentally-friendly approach to farming that promotes the use of natural methods to control pests and diseases, conserve soil and water, and maintain healthy ecosystems. It can provide numerous benefits, including improved soil quality, higher crop yields, and a reduction in harmful chemical residues in food.
On the other hand, healthcare is the field of medicine and public health, which focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases and illnesses. Healthcare professionals work to improve the health and well-being of individuals and populations, and may use a range of interventions, including medication, surgery, and lifestyle changes.
However, there are also potential connections between smart organic farming and healthcare. For example, as mentioned in the previous answer, smart organic farming can help to reduce exposure to harmful chemicals, which can contribute to improved health outcomes. Additionally, organic foods are often richer in nutrients, which can also be beneficial for health.
Furthermore, by promoting sustainable farming practices and reducing the negative impact of agriculture on the environment, smart organic farming can also help to prevent environmental degradation and the spread of zoonotic diseases, which are infectious diseases that can be transmitted between animals and humans. This can in turn help to reduce the burden on the healthcare system by preventing the emergence and spread of new diseases.
In summary, while smart organic farming and healthcare are separate fields, there are potential connections between the two, and promoting sustainable farming practices can have important benefits for public health.
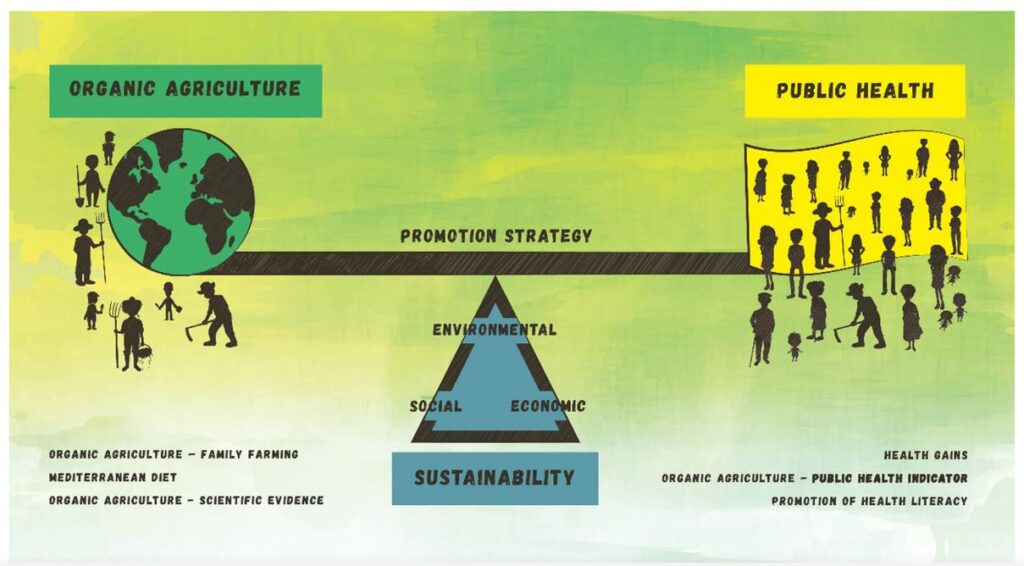
Advantages of Smart Organic Farming in Healthcare:
Reduced use of harmful chemicals: Organic farming uses natural methods to control pests and diseases, which means that there is less exposure to harmful chemicals for both farmers and consumers. This can lead to improved health outcomes and a reduced risk of chronic diseases associated with exposure to pesticides.
Higher nutrient content in crops: Organic farming often results in higher nutrient content in crops due to the use of natural fertilizers and the absence of synthetic pesticides and fertilizers. This can lead to better health outcomes for consumers who consume these crops.
Reduced antibiotic resistance: Organic farming practices promote the use of natural methods to control disease in animals, which can reduce the need for antibiotics. This can help to reduce the prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which is a major public health concern.
Improved air and water quality: Organic farming practices promote the use of natural methods to control pests and fertilize crops, which can help to reduce the amount of chemical runoff that enters water sources. This can lead to improved water quality, which can help to prevent the spread of waterborne illnesses.
Enhanced biodiversity: Organic farming practices often promote biodiversity and the use of natural pest management techniques, which can help to preserve wildlife populations and prevent the spread of diseases between animals and humans.
Overall, smart organic farming can play an important role in promoting better health outcomes for both humans and animals, and can help to reduce the burden on the healthcare industry by preventing the spread of disease and reducing the need for medical interventions.
Disadvantages of Smart Organic farming in Healthcare:
While smart organic farming has many potential benefits for healthcare, there are also some disadvantages to consider. These include:
Lower yields: Organic farming methods may result in lower crop yields compared to conventional farming methods, which could lead to higher prices for organic produce. This may make it more difficult for some consumers to access these healthier options.
Limited availability: Organic produce is not always widely available in some regions, which can limit access to healthier foods for some populations.
Potential for contamination: Organic farming relies heavily on natural methods for pest control, and may be more susceptible to crop contamination from pests and diseases. This could lead to foodborne illness if the produce is not handled and prepared properly.
Higher labor costs: Organic farming often requires more labor-intensive methods, which can lead to higher production costs and potentially higher prices for organic produce.
Certification and regulation: Organic farming requires certification and regulation to ensure that products meet specific standards, which can be a barrier for some farmers who may not be able to afford the certification process.
Limited scalability: Organic farming methods may be more difficult to scale up to large commercial operations compared to conventional farming, which could limit their potential impact on public health and healthcare.
It is important to note that while these disadvantages do exist, they should not be used to dismiss the potential benefits of smart organic farming for healthcare. By addressing these challenges, it may be possible to promote more widespread adoption of sustainable farming practices that can promote better health outcomes for individuals and populations.









